Pablo is a computational physicist with experience in the simulation of black holes and stars collisions, video game AI and automation technology. Currently, Pablo applies his skills to complex medical research problems, including whole-genome sequencing analysis, image processing, molecular dynamics simulations, statistical analysis, and software development.
Current Research
Telomere length and content analysis
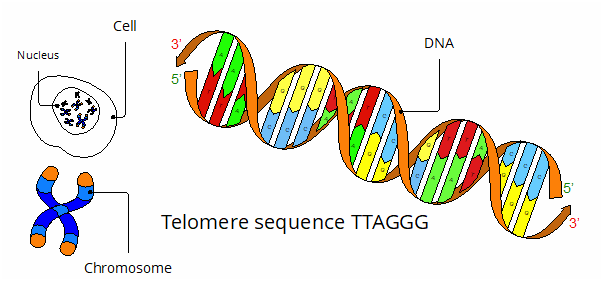
Pablo is using whole-genome sequencing to estimate telomere length and content. Telomeres are protective end-complexes at the termini of eukaryotic chromosomes. Telomeres have the function of capping the ends of chromosomes, preventing them from degradation or fusions with one another. In humans, telomeres consist of repetitive DNA sequence (TTAGGG)n.
Molecular dynamics simulations of shelterin complex proteins and telomeric DNA
Pablo is performing numerical simulations of the shelterin complex proteins and telomeric DNA. The shelterin complex is a group of proteins found specifically at telomeres and is important for maintaining telomere structure and integrity. The shelterin complex is composed of TRF1, TRF2, POT1, TPP1, TIN2 and RAP1. The three main components of shelterin that bind to the DNA directly are TRF1, TRF2 and POT1.